Liao, C.-H.†, & Wu, J.-Y.* (2022). Deploying multimodal learning analytics models to explore the impact of digital distraction and peer learning on student performance. Computers & Education, 104599. (SSCI: 2022 IF: 12.00, Q1)
Abstract
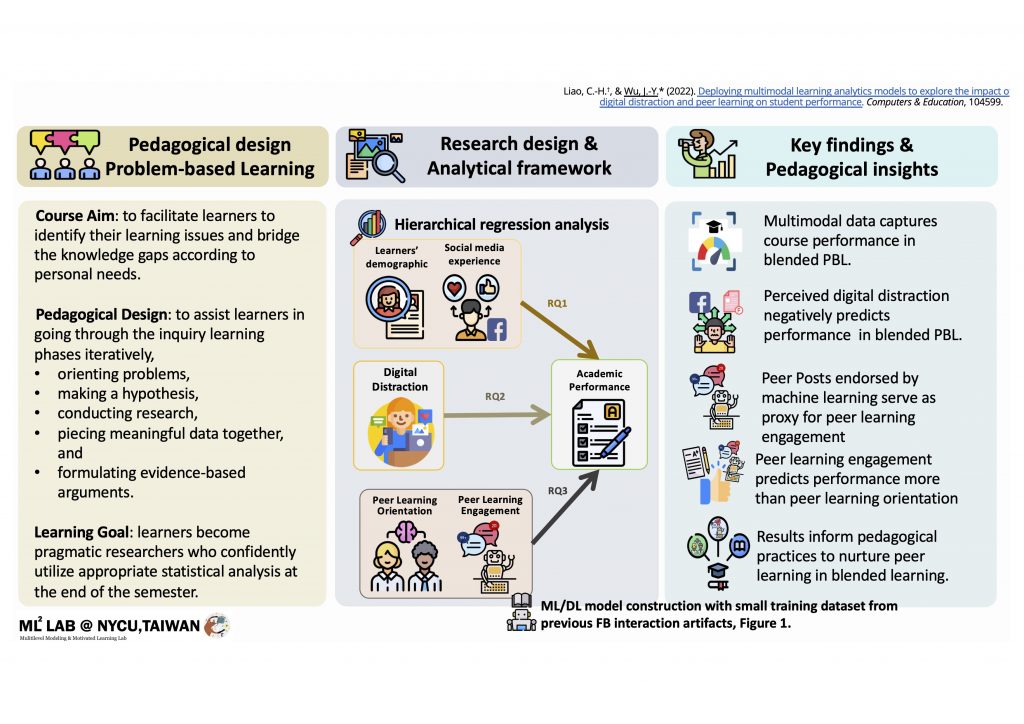
Social media have been extensively incorporated in higher education as an indispensable tool for learning. Nevertheless, research has conflicting findings about its effectiveness due to the highly reported digital distraction and poor peer learning engagement on social media. This study employed an innovative problem-based learning (PBL) pedagogy incorporating Learning Analytics to identify digital distraction, quantify the quality of peer learning engagement, and predict learning performance. Participants were 51 Taiwanese graduate students in blended Statistics courses under the PBL pedagogy. The multimodal Learning Analytics (LA) model contained data from learner discourse on Facebook groups and questionnaires, including learner characteristics, perceived digital distraction, subjective peer learning orientation, and objective peer learning engagement endorsed by machine learning (ML) models. Results showed that students reporting more digital distraction problems obtained lower final course grades, and those reporting stronger peer learning orientation received higher final course grades. Moreover, peer learning engagement objectively recognized by ML models has better predictive validity on academic performance than self-perceived peer learning orientation. The results of the multimodal LA models addressed the scarcity of studies involving learners’ process data in PBL and informed instructional practices and strategies to scaffold students’ statistics learning upon detecting those at risk of distracted attention problems and poor peer learning engagement.
Keywords: Learning analytics, Machine learning, Multimodal data, Digital distraction, Problem-based learning, Peer learning
自述摘要
社交媒體已融入我們的生活,也在各學段的教與學現場中成為當代學習者不可或缺的基本工具。然而,社交媒體上同儕學習的熱絡互動常引來高度的數位分心,往往導致學習者自覺於科技協助的學習歷程中投入度與成效不盡理想。優質教育是實踐各永續發展面向共通利益(co-benefits)的重要基礎。為了提供學生易取得且具質量的教育資源,如何促進學習者於虛實科技學習環境中完成有意義的有效學習等理論與教學基礎研究(fundermental research),亟需資訊教育與數位學習研究和實務工作者來打底。我們越早對此類基礎研究形成問題意識,對實踐形成工作共識,對我們的學生學習就越為有利。但因爲目標族群易受傷害,此類型研究的實驗設計和分析架構的難度極高等等障礙,我們缺乏對於學習者於虛實整合種種面向影響探討的研究,而於實際教與學現場之內,探討學習者參與虛實學習社群(i.e., 個人學習環境(Personal Learning Environment, PLE)自主投入的學習歷程與成效檢驗等教學研究,更為缺稀。
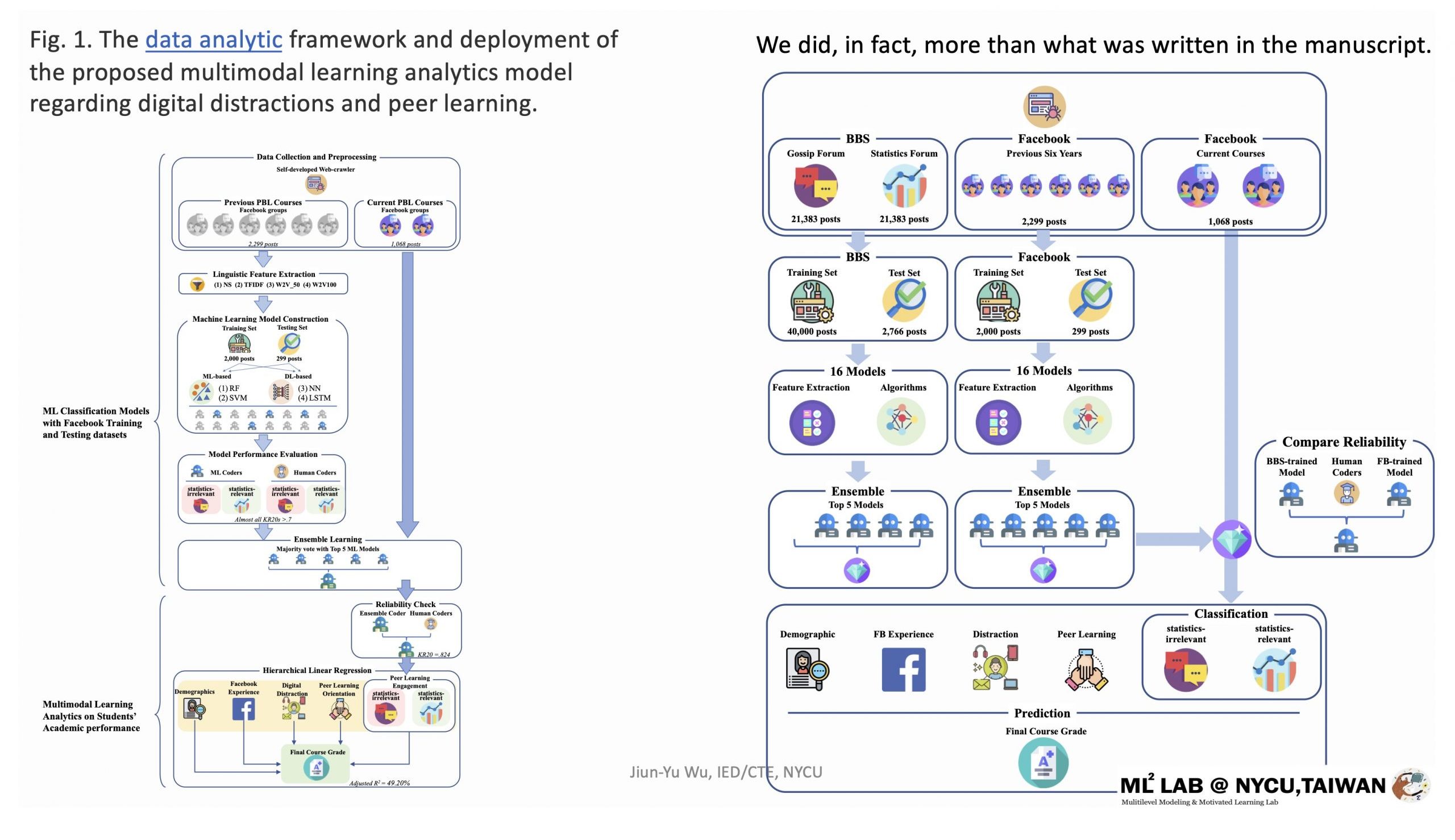
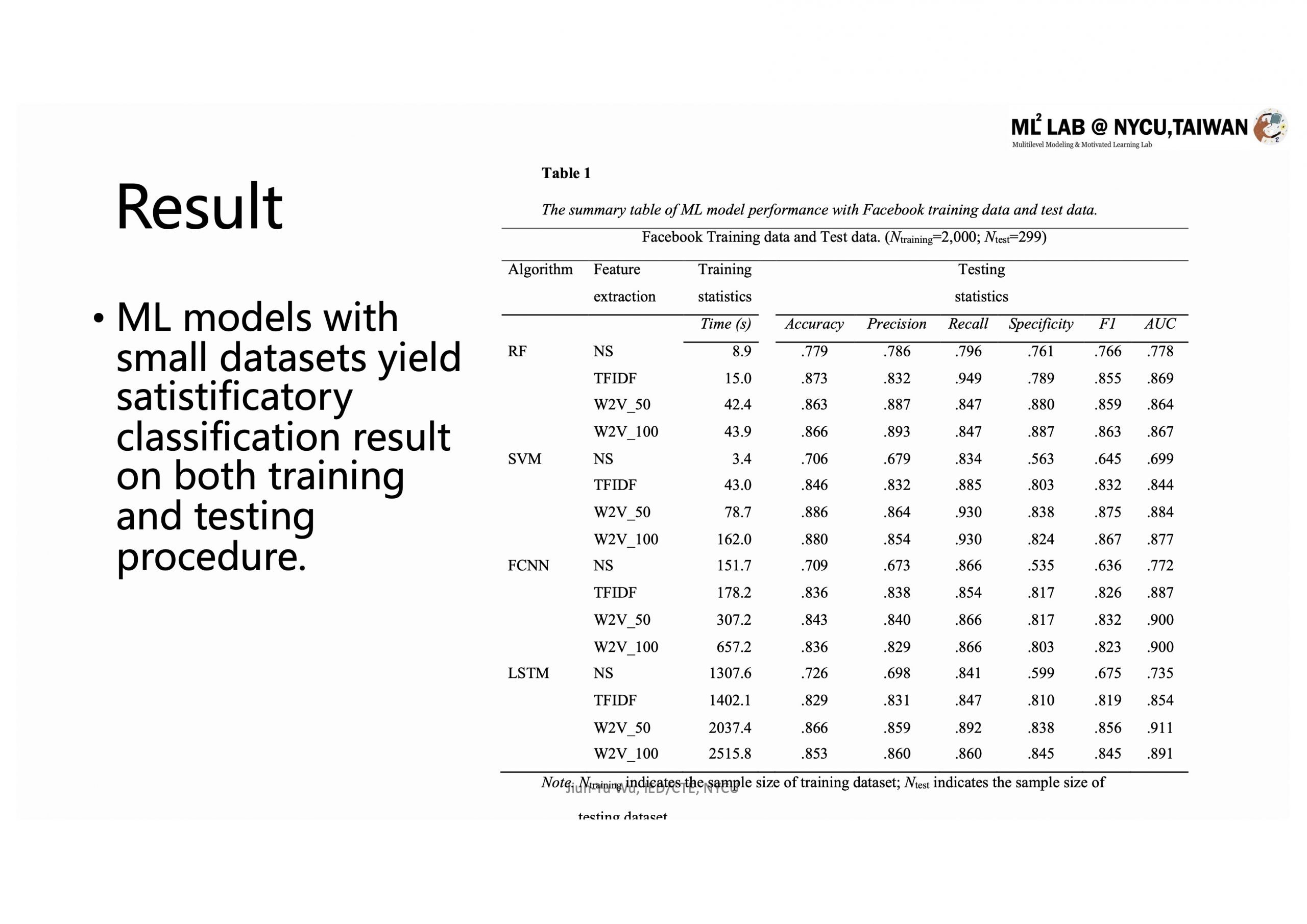
因此,本研究開拓性的進行問題解決導向式學習(Problem-Based Learning, PBL)為期18週的統計課程教學,於IRB核准且遵守APA ethic conduct下,搜集學習者於長時PBL學習中的虛實動態投入與多元評量表現。同時,為完成適用於專業場域的多模態學習分析框架建置,我們突破性採用小樣本訓練資料集,確認了可即時量化於社交媒體中PBL同儕學習認知參與度的客觀量測模組效能,並加入學習者於PBL學習歷程中數位分心與同儕學習的主觀量測反應,總整實現了可預測統計學習者於虛實整合學習環境中的PBL學習歷程與成效表現預測模型。
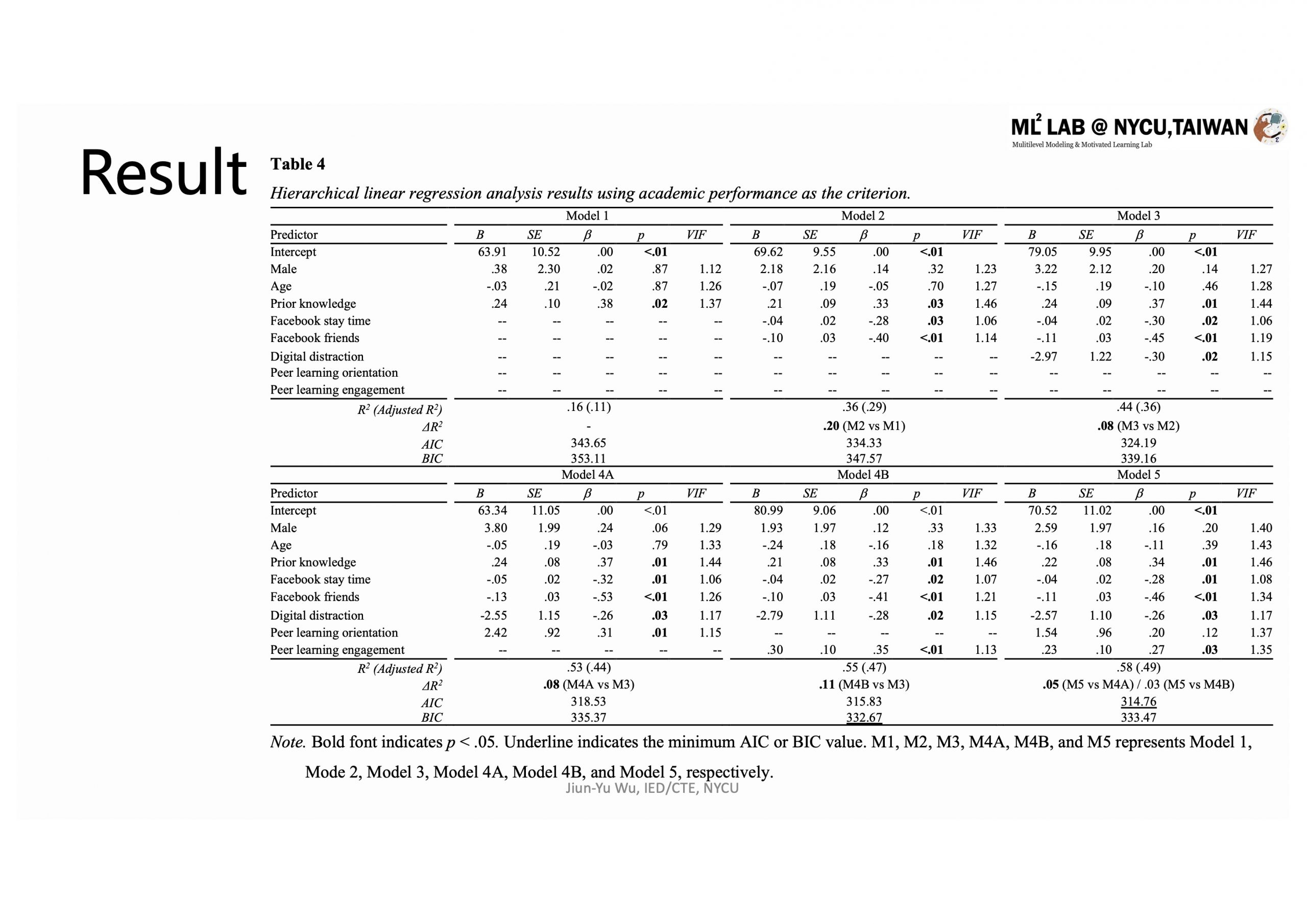
本研究的51名參與者是在PBL教學法下進行混成式統計課程學習的人社領域研究生。準實驗設計與多模態學習分析(LA)模型用於診斷長時學習歷程與成效之間關聯,包含從Facebook學習社群和問卷收集來的學習者歷程數據,包括背景資訊、自陳數位分心問題、同儕學習傾向和由小樣本訓練的監督式機器學習(supervised ML with small training dataet)模型集成的客觀同儕學習參與度。結果顯示,在控制背景資訊與先備能力之後,自陳較多數位分心問題的學生最終課程成績較低,而較高同儕學習傾向的學生可獲得較好的課程成績,不過,由ML模型集成認定的客觀同儕學習參與度對於學生學習表現的預測效力最具實務顯著效果,除了優於自陳的同儕學習傾向以外,更比數位分心問題所帶來的負面影響更為正面有效(i.e., Model 4B in Table 4, ßPeer learning engagement=.35 >ßDigital Distraction=-.28)。
本研究發現數位分心確為今日數位學習的常態問題。為了達成有意義且有效學習的優質教育目標,當代學習者必須具備同儕學習的正向態度,主動參與虛實學習社群互動,並且要積極提供自身學習反思與回饋等同儕學習參與,方可有效使用數位工具進行主動問題解決學習。現場教師更需要增能掌握以上實證發現與應對策略,融入教學設計,以明確協助學習者於複雜學習場域中順利完成學習。此多模態LA基礎研究解決了問題解決導向式學習場景中訓練數據不足的研究困境,實踐了可用於即時預警和診斷的分析模型,搭配對應的教學介入設計,為在虛實科技學習環境中有數位分心問題和同儕學習參與度不佳的學習者,提供了促進其PBL統計學習歷程與成效資量的有效鷹架。
關鍵詞:學習分析、機器學習、多模態數據、數位分心、問題解決導向式學習、同儕學習。